Terraform Quickstart: Part 11 - Debugging and Understanding Terraform Errors
How to Understand and Fix Terraform Errors Without Wasting Hours
Introduction
Even when your code looks correct, Terraform can still fail — with vague errors, confusing messages, or no output at all. Debugging these issues can be frustrating and time-consuming.
In this chapter, you’ll learn practical techniques to troubleshoot Terraform problems. You’ll understand how to read error messages, enable detailed logs, and track down the root cause of failures faster.
📚Do you want to read all lessons in a single pdf? Check out my Terraform Quickstart ebook.
Common Terraform Errors and What They Mean
Validation errors - Something’s wrong in your syntax or variable definitions.
Provider errors (e.g. 401, 403, 404) - Wrong credentials, wrong ID, or missing permissions.
Plan errors - Mismatched inputs or unknown resources.
Apply errors - Cloud provider rejected your request or a dependency failed.
State errors - Corrupted, locked, or outdated
.tfstatefile.
Debugging Techniques
1. Use Terraform’s Built-in Logging
You can enable detailed logs using environment variables:
TF_LOG=DEBUG terraform applyThis outputs detailed logs, including:
HTTP calls to APIs
internal provider behavior
resource planning and evaluation
Levels:
TRACE– very verboseDEBUG– detailed logs (most useful)INFO– normal execution infoWARN/ERROR– filtered messages
2. Log Output to a File
Instead of cluttering your terminal, write logs to a file:
TF_LOG=DEBUG TF_LOG_PATH=debug.log terraform applyThen open debug.log and search for:
Error:linesAuthorization:orAPIresponsesUnexpected
nil,null, or empty values
3. Use terraform state to Inspect State
If your resource exists but Terraform can't find it:
$ terraform state listTo inspect a specific resource:
terraform state show <resource_address>Useful when something seems out of sync.
4. Check Provider Docs and API
If Terraform says “resource not found” or “invalid argument,” the issue may be with the cloud API, not Terraform. Look up the official provider documentation to check:
Required and optional arguments
Import formats
Supported values and constraints
5. Try Minimal Examples
If a resource block keeps failing, reduce it to the smallest working example. This helps isolate whether the problem is:
with the values
with dependencies
or with the Terraform config itself
6. Watch for State Drift
Sometimes Terraform's state no longer matches the real world. Symptoms:
Terraform tries to delete and recreate unchanged resources
terraform planlooks wrongImport doesn’t work
Common fixes:
Re-import the resource
Run
terraform refreshManually update state with
terraform state mvorstate rm(careful!)
7. Use terraform console
You can interactively evaluate expressions:
$ terraform console
> var.repo_name
> local.tags
> aws_instance.my_app.public_ipConclusion
In this lesson, you learned tips and best practices to read and recognise Terraform errors.
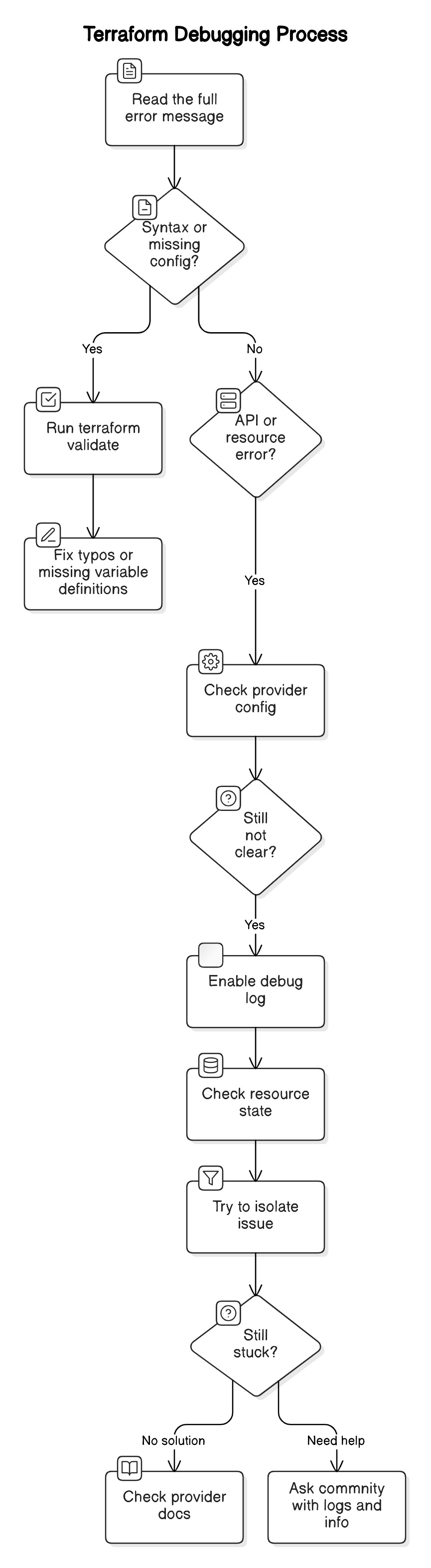
Refer to this debugging path when you feel stuck:
Remember to always break down the problem into smaller pieces.